genetics

July 1, 2022
#IAmScience: Ajay Gupta
By Cara Penquite | Bond LSC Photo by Cara Penquite | Bond LSC Ajay Gupta learned biology basics as a first year undergraduate on the bumpy bus ride from his small hometown to Punjab Agricultural University. Just a few hours’ ride, he made the most of his time before he returned home to help his family’s agricultural goods business. Working extra hours in the margins of his time has become a habit for Gupta. Now a plant science first year Ph.D. student in the Bing Yang lab and Department of Plant Science and Technology Millikan Endowment…

March 3, 2022
Protecting Plants: Researchers identify genes responsible for vital antimicrobial proteins
DNA is the genetic material that determines the characteristics of plants and animals. Using CRISPR gene editing, researchers altered the characteristics of rice plants. | Creative Commons Photo by Pixabay By Cara Penquite | Bond LSC A tickle in the throat, a stuffy nose, congestion . . . the tell-tale signs of a cold are familiar to most, and many know that with enough rest, the immune cells on standby in the human body will destroy any invaders. But what happens when plants get sick? The Bing Yang Lab from the Bond Life Sciences Center at the…

Feb. 2, 2022
Outlining Omicron: researchers determine key mutations in the latest COVID-19 variant
Bond LSC and UNMC scientists explain mutations unique to the Omicron variant Austin Spratt, undergraduate mathematics student in the Kamlendra Singh lab, shows protein models of the Omicron spike protein and the receptor it attaches to when infecting cells. “The genetic codes are used to identify the mutations, and then we use the structure to see how it would change over time. It’s going to give us more information about new mutations that occur,” Spratt said. | Photo by Cara Penquite, Bond LSC By Cara Penquite | Bond LSC It took eight days for…

July 21, 2016
Finding hope by fixing a gene
Lorson lab publishes research on a new therapeutic path to help treat spinal muscular atrophy By Phillip Sitter | MU Bond Life Sciences Center Erkan Osman shows iImages of neuro-muscular junctions. Osman, a post-doctoral fellow in Chris Lorson’s lab, co-authored research in the journal Molecular Therapy that details work in binding a synthetic nucleic acid to a normally useless motor neuron backup gene to help treat spinal muscular atrophy. | photo by Phillip Sitter, Bond LSC Imagine you are forced to jump out of an airplane. Luckily, you find a parachute that even…

March 1, 2016
Unmasking the unknown
Scientists explore genetic similarities between plants and mice University of Missouri PhD Candidate Daniel L. Leuchtman peers through an Arabidopsis plant. Leuchtman has been experimenting with replacing a gene in the plants immune system with a similar gene from mice. | Photograph by Justin L. Stewart/MU Bond Life Sciences Center By Justin L. Stewart | MU Bond Life Sciences Center Almost two-thirds of what makes a human a human and a fly a fly are the same, according to the NIH genome research institute. If recent research at the University of Missouri’s Bond…
Oct. 8, 2015
Understanding spit
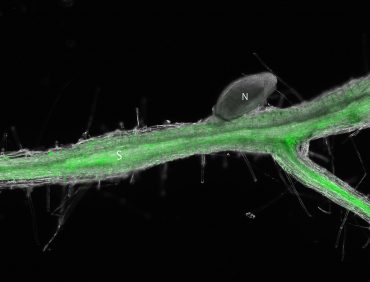
Scientists find how nematodes use key hormones to take over root cells Roger Meissen | Bond Life Sciences Center This Arabidopsis root shows how the beet cyst nematode activates cytokinin signaling in the syncytium 10 days after infection. The root fluoresces green when the TCSn gene associated with cytokinin activation is turned on because it is fused with a jellyfish protein that acts as a reporter signal. (N=nematode; S=Syncytium). Contributed by Carola De La Torre This is a story about spit. Not just any spit, but the saliva of cyst nematodes, a parasite that literally sucks…

June 22, 2015
Scientists uncover how caterpillars created condiments
The next time you slather mustard on your hotdog or horseradish on your bun, thank caterpillars and brassica for that extra flavor. While these condiments might be tasty to you, the mustard oils that create their flavors are the result of millions of years of plants playing defense against pests. But at the same time, clever insects like cabbage butterflies worked to counter these defenses, which then started an arms race between the plants and insects. An international research team led by University of Missouri Bond Life Sciences Center researchers recently gained insight into a genetic basis for this co-evolution…

June 10, 2014
SoyKB: Leading the convergence of wet and dry science in the era of Big Data
Yaya Cui, an investigator in plant sciences at the Bond Life Sciences Center examines data on fast neuron soybean mutants that are represented on the SoyKB database. The most puzzling scientific mysteries may be solved at the same machine you’re likely reading this sentence. In the era of “Big Data” many significant scientific discoveries — the development of new drugs to fight diseases, strategies of agricultural breeding to solve world-hunger problems and figuring out why the world exists — are being made without ever stepping foot in a lab. Developed by researchers at the Bond Life…