Research

Jan. 11, 2017
Cornelison receives highest honor from White House
It feels good to get recognition, especially when it comes from the White House. This week D Cornelison, a Bond Life Sciences Center researcher and associate professor of biological sciences found out she will receive a Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers (PECASE). The award is the highest honor bestowed by the United States government on science and engineering professionals in the early stages of their independent research careers. She joins 102 researchers this year selected by the White House to receive this prestigious award. This is a first for Missouri as a state…

Nov. 17, 2016
Live long and prosper: healthy mitochondria, healthy motor neurons?
Chris Lorson (front) and Mark Hannink (back) collaborate to study the role of mitochondria in motor neuron health, particularly in relation to spinal muscular atrophy, a neuromuscular disorder | photo by Jen Lu, Bond LSC Chris Lorson, a professor of veterinary pathobiology, and Mark Hannink, a professor of biochemistry, want to find a new way to help motor neurons live a long and healthy life. Their question: what’s the relationship between motor neuron sruvival and a cellular component called mitochondria? The two researchers at the Bond Life Sciences Center were awarded preliminary funding from the Bond…

Nov. 4, 2016
The eyes have it
Bond LSC scientist works with MU eye surgeon to help people suffering from autoimmune-disease Sjögren’s syndrome By Phillip Sitter | Bond LSC Dr. Carisa Petris stands in the McQuinn atrium of Bond Life Science Center. She and Bond LSC researcher Gary Weisman are using funding from a $100,000 Bond LSC grant to study the mechanisms of an auto-immune disease in the lacrimal glands of the eyes. They are hoping treatments for the disease in mice they study could be applied to humans. | photo by Phillip Sitter, Bond LSC They may not get much…

Oct. 25, 2016
Close encounters of the plant protein kind
Bond LSC researchers David Mendoza (left) and Scott Peck (right) are collaborating to develop a new method for studying protein signaling pathways inside plant cells. | photo by Jennifer Lu, Bond LSC By Jennifer Lu | Bond LSC Sometimes, timing is everything. That was the case in what led to a new collaboration between the Mendoza and Peck laboratories. The two researchers were recently awarded $48,250 in seed money from the Bond Life Sciences Center to adapt a new technology to the study of signaling pathways in plant cells. David Mendoza, a Bond LSC researcher and…

Oct. 11, 2016
The seeds of progress
Efforts to understand the genome of one plant through its many genetic varieties could lead to nutritional improvements in the staple crops billions of people depend on By Phillip Sitter | Bond LSC Ruthie Angelovici stands next to some Arabidopsis thaliana samples in the basement of Bond LSC. She is leading projects to study the relationships between genotypic and phenotypic variation in Arabidopsis and how this affects the amino acid content of the plants, and the resistance of their seeds to drought conditions. | Phillip Sitter, Bond LSC It’s hard to avoid corn, rice or soybeans…

Oct. 10, 2016
Expert Comment: How science made the “three-person” baby possible
Stock image via iStock By Jennifer Lu | Bond LSC A new in-vitro fertilization technique that uses genetic material from three persons made the news last week following the announcement of the successful birth of a now five-month-old baby boy. The process allowed the mother, who had a rare mitochondrial disease known as Leigh Syndrome, to have a child without passing her faulty mitochondrial genes. The nucleus from the mother’s egg was inserted into a prepared donor egg that had healthy mitochondria to make a cybrid, or cytoplasmic hybrid, egg that was then fertilized.
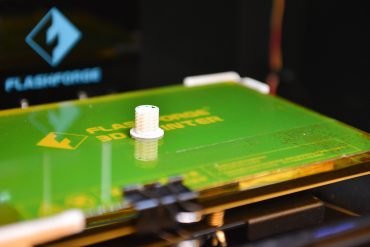
Sep. 28, 2016
An enzymatic future
Inter-departmental MU team aims to improve enzyme use and recovery for spectrum of industrial, medical and military applications By Phillip Sitter | Bond LSC A mostly-finished cylindrical bio-reactor site sits in a 3D printer after the printing has stopped. With a 3D printer in-house, Chung-Ho Lin said that the inter-departmental team he is part of can generate four or five different prototypes a day to test in their bio-reactor model, instead of having to order from different fabrication companies. A basic printer like this used to cost $8,000, but within the last year prices dropped to…

Sep. 2, 2016
Building blocks of life in the lab could revolutionize life for us all
NASA, NIH-funded work seeks to understand bio-chemical mechanisms of life on Earth, and among the stars By Phillip Sitter | Bond LSC Donald Burke-Agüero stands in his office in Bond LSC, holding a model of an RNA protein structure. Burke-Agüero studies the bio-chemical functions of RNA, and how those functions might be able to be artificially designed or replicated. | Phillip Sitter, Bond LSC Any child obsessed with Legos knows the fun of creation bound only by imagination and the size or variety of the blocks within their pile. For some scientists, that spirit extends…

Aug. 4, 2016
Standing out through saliva
Bond LSC scientist internationally recognized for work on salivary glands and autoimmune disorders By Phillip Sitter | Bond LSC You might not think too highly of spit, but you would quickly regret not having any. People with Sjögren’s syndrome suffer chronic dry mouth and eyes from an overzealous immune system that attacks salivary and tear ducts, causing serious health issues. Gary Weisman’s research might hold the key to understanding and managing this immune response, leading to effective treatment or even prevention of this ailment. For this, the International Association of Dental Research, or IADR, awarded him the 2016 Distinguished Scientist Award…

July 21, 2016
Finding hope by fixing a gene
Lorson lab publishes research on a new therapeutic path to help treat spinal muscular atrophy By Phillip Sitter | MU Bond Life Sciences Center Erkan Osman shows iImages of neuro-muscular junctions. Osman, a post-doctoral fellow in Chris Lorson’s lab, co-authored research in the journal Molecular Therapy that details work in binding a synthetic nucleic acid to a normally useless motor neuron backup gene to help treat spinal muscular atrophy. | photo by Phillip Sitter, Bond LSC Imagine you are forced to jump out of an airplane. Luckily, you find a parachute that even…

July 19, 2016
How does Zika move from mother to child?
Scientists use placental cells in lab to study virus By Phillip Sitter | MU Bond Life Sciences Center Megan Sheridan, an MU grad student, removes the base solution from a demonstrated sample of stem cells that will be grown into placental cells for study of Zika virus. Within four days of exposure to the correct hormones, the stem cells express genes of placental cells, and within another day start producing placental hormones. The cells are infected with Zika at day four to ensure maximum measurable interaction, as the stem cells naturally die in…

July 6, 2016
Anthrax: villain or misunderstood?
Stewart holds a different colony of anthrax in his lab. Stewart’s work with anthrax and other similar organisms focuses on understanding the tough protein shell of the bacteria’s spores that enable the pathogen to survive in soil for extended periods of time, even hundreds of years. | photo by Phillip Sitter, Bond LSC By Phillip Sitter | MU Bond Life Sciences Center For a tiny spore, anthrax holds a lot of danger and promise. If you found yourself wondering about more than its safety in the lab, we have a answers to a few persistent…