News

April 28, 2014
A drug that packs a punch: new compound works better against resistant HIV
Bond LSC researcher Stefan Sarafianos stands in the LSC atrium. The virologist is an associate professor of molecular microbiology and immunology and Chancellor’s Chair of Excellence in Molecular Virology with appointments in MU’s School of Medicine and the Department of Biochemistry. Resistance is the price of success when it comes to treating HIV. Virologists at the Bond Life Sciences Center are helping to test the next generation of anti-AIDS medication to quell that resistance. Stefan Sarafianos’ lab recently proved that EFdA, a compound that stops HIV from spreading, is 70 times more potent against some HIV…

April 25, 2014
Frogs help researchers find genetic mechanism for mildew susceptibility in grapevine
Powdery mildew on a cabernet sauvignon grapevine leaf. | USDA Grape genetics publications and research A princess kisses a frog and it turns into a prince, but when a scientist uses a frog to find out more information about a grapevine disease, it turns into the perfect tool narrowing in on the cause of crop loss of Vitis vinifera, the world’s favorite connoisseur wine-producing varietal. MU researchers recently published a study that uncovered a specific gene in the Vitis vinifera varietal Cabernet Sauvingon, that contributes to its susceptibility to a widespread plant disease, powdery mildew.
April 24, 2014
Chemical beacons: LSC scientist discovers how plants beckon bacteria to attack
Scott Peck, Bond LSC scientist and associate professor of biochemistry, studies Arabidopsis and how bacteria perceive it before initiating an infection. Roger Meissen/ Bond LSC Sometimes plants inadvertently roll out the red carpet for bacteria. Researchers at the University of Missouri Bond Life Sciences Center recently discovered how a plant’s own chemicals act as a beacon to bacteria, triggering an infection. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences published their study April 21. “When bacteria recognize these plant chemicals it builds a needle-like syringe that injects 20-30 proteins into its host, shutting down the plant’s…

April 22, 2014
Bond LSC Investigator Chris Pires in Shanghai, Wuhan
Recently, one of our investigators, J. Chris Pires traveled to Fudan University in Shanghai and the Wuhan Vegetable Research Institute for the 19th annual Crucifer Genetic Workshop and Brassica 2014 Conference in Wuhan, China. Pires was invited to the esteemed event as the keynote speaker of the Brassica Conference. He led workshops as part of the three-day conference March 30 through April 2 and also visited Fudan University in Shanghai during the trip. Pires is an associate professor in biological sciences and focuses much of his research on the evolution of plants. His talk at Fudan University discussed his research…

March 25, 2014
Bond LSC staff prepares boat for April 12 fundraiser
Made completely of cardboard and Popeye themed, Bond LSC facilities crew say this boat could be the winner of the 3rd Annual Flot Your Boat for the Food Bank Race on April 12 — BLANKENBUEHLER Every year the College of Agriculture, Food and Natural Resources puts on a Float Your Boat for the Food Bank Race. All proceeds go to the Columbia Food Bank and last year, with 45 participants, more than $17,000 was donated. All participants craft their own boat and obey one golden rule: cardboard only. The Bond LSC crew are returning to…

March 25, 2014
Choi honored for distinguished dissertation
Jeongmin Choi (left), Gary Stacey (center) and postdoc Kiwamu Tanaka recently discovered the first plant receptor for extracellular ATP. Choi received the 2014 Distinguished Dissertation Award for her part in this work. A former Bond LSC graduate student is being recognized for a dissertation that stands out from the crowd. Jeongmin Choi received the 2014 Distinguished Dissertation Award this month from MU’s Graduate Faculty Senate for her work identifying the first plant receptor for extracellular ATP. The journal Science published Choi’s “Identification of a plant receptor for extracellular ATP” Jan. 17, 2014. Choi completed her dissertation working as…
March 21, 2014
MU researchers find key gene in spinal locomotion, yield insight on paralysis
Samuel Waters and graduate researcher Desiré Buckley review stages of embryonic development. — BLANKENBUEHLER The difference between walking and being paralyzed could be as simple as turning a light switch on and off, a culmination of years of research shows. Recently, University of Missouri Assistant Professor of biology Samuel T. Waters isolated a coding gene that he found has profound effects on locomotion and central nervous system development. Waters’ work with gene expression in embryonic mouse tissue could shed light on paralysis and stroke and other disorders of the central nervous system, like Alzheimer’s disease. Waters…

March 11, 2014
Strong symposium start by Skloot
Karin Loftin, MU Chancellor R. Bowen Loftin, Bond Life Sciences Director Jack Shultz and Tim Evans pose with Rebecca Skloot at the University of Missouri Monday evening — BLANKENBUEHLER The bridge between public knowledge and the inner-workings of the science community is one that many are reluctant to cross. Sometimes riddled with confusing terms, the most exciting discoveries aren’t always approachable. The 10th annual MU Life Sciences & Society Symposium began Monday evening with Rebecca Skloot as she spoke to a nearly full house at Jesse Auditorium Monday. Every year the symposium erases the line between community…
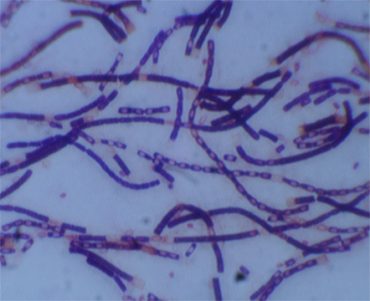
Feb. 7, 2014
Quicker anthrax detection could save millions of dollars, speed bioterror response
Anthrax bacteria is a rod-shaped culture. Most common forms of transmission are through abrasions in the skin and inhalation. Imagine researchers in hazmat suits moving slowly and deliberately through a lab. One of them holds up a beaker. It’s glowing. This light — or the absence of it — could save millions of dollars for governments and save the lives of anthrax victims. Scientists at the University of Missouri Laboratory of Infectious Disease Research proved a new method for anthrax detection can identify anthrax quicker than any existing approach. When the “bioluminescent reporter phage” —…

Feb. 3, 2014
Mind map: Bond LSC research explains how proteins guide migrating neurons
Bond LSC scientist Anand Chandrasekhar studies the zebrafish model to learn how motor neurons develop. These adult zebrafish lay eggs used to gain insight into how motor neurons arrange themselves as embryos grow into adults. Roger Meissen/ Bond LSC Three thousand zebrafish swim circles in tanks located on the ground floor of the Bond Life Sciences Center, content to mindlessly while away their existence by eating their fill and laying eggs. Despite their very basic higher functions, Bond LSC researcher Anand Chandrasekhar wants to understand how their brains work. More importantly, he wants to know how individual…

Jan. 16, 2014
Bond LSC team identifies first plant receptor for extracellular ATP
Jeongmin Choi (left), Gary Stacey (center) and Kiwamu Tanaka recently discovered the first plant receptor for extracellular ATP using Arabidopsis plants. Roger Meissen/Bond LSC It’s the genetic equivalent to discovering a new sensory organ in plants. A team at the University of Missouri Bond Life Sciences Center found a key gene that sniffs out extracellular ATP. Scientists believe this is a vital way plants respond to dangers, such as insects chewing on its leaves. The journal Science published their research Jan. 17. “Plants don’t have ears to hear, fingers to feel or eyes to see. They recognize…

Jan. 13, 2014
Bond LSC researchers search for causes of complex pregnancy disorder
Toshihiko Ezashi (left), Danny Schust (middle), Laura Schulz (middle) and Michael Roberts (right) collaborate on new research to discover the causes of preeclampsia. Roger Meissen/ Bond LSC You can’t see the resemblance, but cells in Michael Roberts’ lab share a family tree with some newborns. Their common genetics may help explain severe, early-onset preeclampsia, an inherited disorder that leads to a placenta that is often small and inefficient and possibly due to the mother’s body not fully welcoming her pregnancy. University of Missouri Health Center scientists such as Danny Schust and Laura Schulz, work with Roberts and…