Arabidopsis

April 29, 2022
#IAmScience: Mengran Yang
By Cara Penquite | Bond LSC Mengran Yang sat perched on a stool too tall for the cart of lush green tobacco plants in front of her. Behind towering shelves of lab equipment, she hunched over the plants and steadily pricked each leaf with a syringe. Yang works with Arabidopsis and tobacco plants to learn about plant immune systems as a postdoctoral fellow in the Gary Stacey lab. Her research focuses on signals plant cells send to coordinate a fight against pathogens. “I think it’s very interesting to see how plants can defend against the pathogens,”…

March 1, 2016
Unmasking the unknown
Scientists explore genetic similarities between plants and mice University of Missouri PhD Candidate Daniel L. Leuchtman peers through an Arabidopsis plant. Leuchtman has been experimenting with replacing a gene in the plants immune system with a similar gene from mice. | Photograph by Justin L. Stewart/MU Bond Life Sciences Center By Justin L. Stewart | MU Bond Life Sciences Center Almost two-thirds of what makes a human a human and a fly a fly are the same, according to the NIH genome research institute. If recent research at the University of Missouri’s Bond…
Oct. 8, 2015
Understanding spit
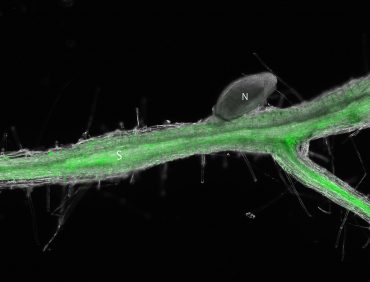
Scientists find how nematodes use key hormones to take over root cells Roger Meissen | Bond Life Sciences Center This Arabidopsis root shows how the beet cyst nematode activates cytokinin signaling in the syncytium 10 days after infection. The root fluoresces green when the TCSn gene associated with cytokinin activation is turned on because it is fused with a jellyfish protein that acts as a reporter signal. (N=nematode; S=Syncytium). Contributed by Carola De La Torre This is a story about spit. Not just any spit, but the saliva of cyst nematodes, a parasite that literally sucks…

Nov. 20, 2014
“Mutant seeds” blossom in the pollen research field
A mutant arabidopsis model nearing pollination. Mutant arabidopsis models under lamps in Shuqun Zhang’s lab. Three-month-old mutant arabidopsis models are used to study the function of pollen. The thought of pollen dispersed throughout the air might trigger horrific memories of allergies, but the drifting dander is absolutely essential to all life. Science has long linked this element of reproduction with environmental conditions, but the reasons why and how pollen functions were less understood. Now lingering questions about the nuanced control of plants are being answered. “Pollen is a very important part of the reproductive process and…

July 1, 2014
Hearing danger: predator vibrations trigger plant chemical defenses
Experiments show chewing vibrations, but not wind or insect song, cause response As the cabbage butterfly caterpillar takes one crescent-shaped bite at a time from the edge of a leaf, it doesn’t go unnoticed. This tiny Arabidopsis mustard plant hears its predator loud and clear as chewing vibrations reverberate through leaves and stems, and it reacts with chemical defenses. Plants have long been known to detect sound, but why they have this ability has remained a mystery. University of Missouri experiments mark the first time scientists have shown that a plant responds to an ecologically relevant sound in its environment. “What…
April 24, 2014
Chemical beacons: LSC scientist discovers how plants beckon bacteria to attack
Scott Peck, Bond LSC scientist and associate professor of biochemistry, studies Arabidopsis and how bacteria perceive it before initiating an infection. Roger Meissen/ Bond LSC Sometimes plants inadvertently roll out the red carpet for bacteria. Researchers at the University of Missouri Bond Life Sciences Center recently discovered how a plant’s own chemicals act as a beacon to bacteria, triggering an infection. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences published their study April 21. “When bacteria recognize these plant chemicals it builds a needle-like syringe that injects 20-30 proteins into its host, shutting down the plant’s…