News

April 20, 2022
Protein or Poison? Research into seed composition shows potential uses as protein source or insecticide
Hari Krishnan holds a handful of A. pavonina seeds. Known for their bright color, the seeds are known among many Asian and African communities as coming from the red bead tree. Photo by Cara Penquite | Bond LSC By Cara Penquite | Bond LSC An energetic and fulfilling day starts with a spread of healthy meals, and many people rely on nutrition labels to meet their daily quota of vitamins and nutrients. But how did scientists measure the Vitamin C in an orange or the protein content in peanuts for the label? Finding out…

April 15, 2022
#IAmScience: Aijing Feng
By Cara Penquite | Bond LSC Growing up in a humble beach town in China, Aijing Feng dreamed of following the footsteps of her idol and Microsoft co-founder Bill Gates. Now halfway around the globe nimbly tapping a keyboard in her cubicle at the Bond Life Sciences Center, she realizes the shortcomings of her tech-giant fantasy. “For a commercial thing, you can have lots of money, you can earn lots of money, you can have [a] great life,” Feng said. “But when you [do] research, you can have ideas [that] something can change in your life.

April 13, 2022
Receptors Found to Help Patients with Sjögren’s Disease
The Baker lab poses for a group photograph. The lab has been working with specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators in efforts to help patients with Sjögren’s Disease. Photo by Karly Balslew, Bond LSC By Karly Balslew | Bond LSC Saliva is probably not the first thing that comes to mind when we think about eating our favorite foods. The clear liquid washes away food debris and bacteria, and it plays a vital role in maintaining our dental hygiene and oral health. You may take it for granted, but for patients with Sjögren’s disease, life without saliva is…

April 8, 2022
#IAmScience: Dong Xu
Data connects all: ‘Champion collaborator’ Xu bridges research disciplines with bioinformatics By Cara Penquite | Bond LSC Dong Xu extracts wonder from numbers with a keyboard and eager teams of scientists at his fingertips. With his salt-and-pepper hair visible above the cubicle walls and his voice softly but steadily articulated, the beauty of bioinformatics takes shape in his mind although it might not be inherently evident in the rows of computers tucked into a small first floor lab. Xu weaves a multifaceted masterpiece of research methodologies and makes sense of a sea of data from cell…

March 25, 2022
#IAmScience: Kathryn Vanden Hoek
By Karly Balslew | Bond LSC Kathryn Vanden Hoek proves that it is never too early to dive into research if you have a passion for it. The undergraduate research assistant started hands-on research her freshman year through the Freshman Research in Plants Programs (FRIPS). This program introduces new students to plant research and exposes them to a lab setting. She matched with the Chris Pires lab at Bond LSC in January of 2021. “I absolutely love it,” Vanden Hoek said. “I knew for a long time that I wanted to do research, so…

March 24, 2022
Bond Welcomes New Principal Investigator John Driver
Photo by Roger Meissen By Karly Balslew | Bond LSC Pigs may have a reputation for being lazy and dirty but to immunologist John Driver, they are the key to understanding influenza in humans. “Pigs are a great animal to study influenza in because they are susceptible to getting the flu,” Driver said. “They are like a mixing vessel for influenza viruses.” Swine have their own strains of influenza virus but can also contract strains from other species like birds and humans. When that happens, these different flu viruses can recombine…

March 18, 2022
#IAmScience: Jiude Mao
By Cara Penquite | Bond LSC Learning has no borders for Jiude Mao. His inquisitive mindset drives him to cross research disciplines and countries chasing the answers to his questions. Mao studies mutations in the gene Ighmbp2 that result in spinal muscular atrophy with respiratory distress type one (SMARD1) and Charcot Marie Tooth 2S (CMT2S) in the Chris Lorson lab. Mao’s research attempts to better understand the effects that different mutations have on disease severity and progression that could help develop treatment options to alleviate disease symptoms. The idea of finding treatment for a genetic disease…
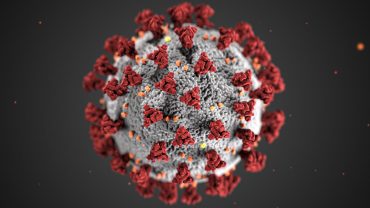
March 16, 2022
Competing with COVID: Researcher suggests varying from vaccines to fight virus
COVID-19 virus particles have spike proteins, represented in red, that attach to receptors on host cells. Antivirals block the receptors on host cells so the virus cannot infect more cells. | Creative Commons Photo By Cara Penquite | Bond LSC Vaccines were the light at the end of the tunnel throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, but virus mutations threaten to extinguish hope of a quick end to the pandemic. Kamlendra Singh turns towards antivirals as the next step. “There will be a time we will find an antiviral which will be very difficult for the virus to mutate…

March 11, 2022
#IAmScience: Juliette Baker
By: Karly Balslew | Bond LSC Science and art may feel like completely separate departments but for research scientist Juliette Baker, this couldn’t be further than the truth. Her mom is a graphic designer and fueled her passion for art while Baker’s own love for science fused the two worlds together. She even drew a diagram for her master’s thesis on Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS). “Honestly, people don’t think science and art overlap a ton,” Baker said. “But, I’m making tons of schematics for people to understand, and it’s all my artistic brain, really.”…

March 4, 2022
#IAmScience: Lynden Voth
By Cara Penquite | Bond LSC Invested in two to three hobbies at a time, Lynden Voth is not afraid to try something new. His flexible mindset – applied equally in his personal life and research – led Voth to discover his passion for molecular pathogenesis and therapeutics. “I was kind of in a completely different headspace when I first came here, and then as I started to do some research and understand what the labs were working on, I ultimately found an interest that I was not aware of before,” Voth said. Voth is a second-year…

March 3, 2022
Protecting Plants: Researchers identify genes responsible for vital antimicrobial proteins
DNA is the genetic material that determines the characteristics of plants and animals. Using CRISPR gene editing, researchers altered the characteristics of rice plants. | Creative Commons Photo by Pixabay By Cara Penquite | Bond LSC A tickle in the throat, a stuffy nose, congestion . . . the tell-tale signs of a cold are familiar to most, and many know that with enough rest, the immune cells on standby in the human body will destroy any invaders. But what happens when plants get sick? The Bing Yang Lab from the Bond Life Sciences Center at the…

Feb. 25, 2022
#I Am Science Mariam Teme
By: Karly Balslew | Bond LSC Mariam Teme’s passion for plants started while growing up in Mali, West Africa, as she watched her father — an agricultural economist — interact with plants daily in the lush area where she grew up. “It’s like my own little bubble of peace when I’m surrounded by plants,” Teme said. Teme, now a member of the Bing Yang lab, planned to study agriculture for her bachelor’s degree but her university in Istanbul, Turkey, only offered genetics and bioengineering. However, integrated it with plant life for her future career. “I thought…